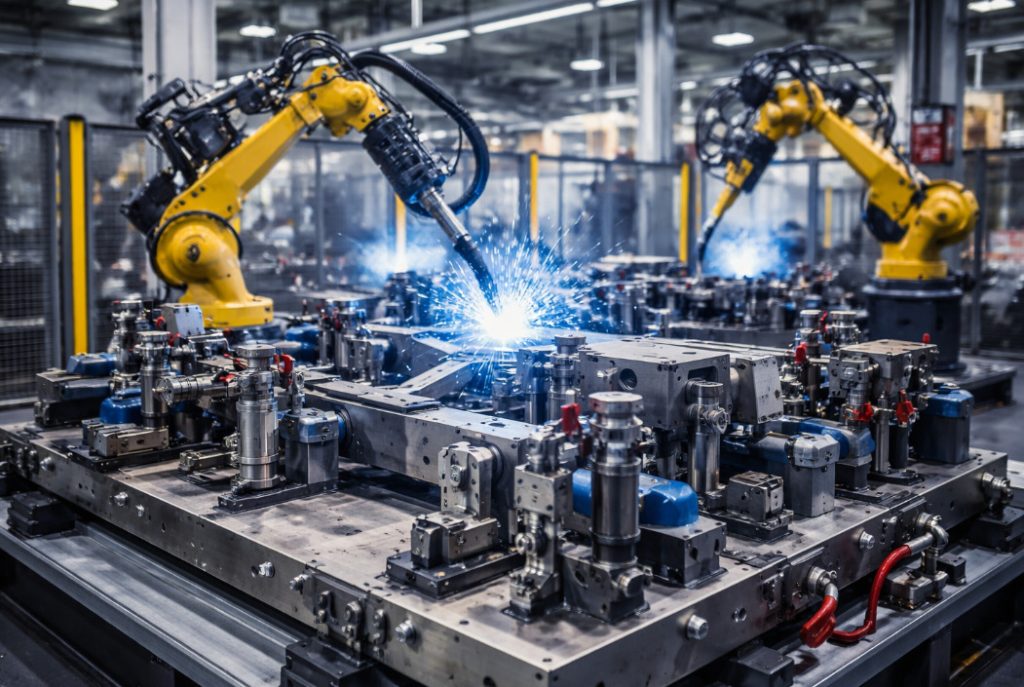
Welding Fixture Design and Robotic Welding Cell Engineering for Automotive and Rail Systems
In today’s automotive and rail system industries, the efficiency of production lines, quality stability, and cycle times depend directly on welding fixture design, robotic welding cell design, and process engineering capabilities. Especially in high-precision mass production projects, a properly designed fixture system and a well-engineered robotic welding cell are among the most critical factors determining overall production performance.
Why Is Welding Fixture Design Critical?
Welding fixture design ensures that parts are positioned accurately during production, enabling repeatable and consistent quality. In automotive fixture design and rail system fixture design projects, proper tolerance management, referencing strategies, and correct clamping force selection are essential for maintaining dimensional stability after welding.
A welding fixture designed with the right engineering approach provides the following advantages:
- Dimensional stability in mass production
- Reduced scrap rates
- Shorter cycle times
- Stable process performance in robotic welding lines
- Improved operator ergonomics
- Reduced maintenance and service time
For this reason, welding fixture design in modern manufacturing facilities is not only a mechanical equipment development activity but also a comprehensive process engineering discipline.
Modern Welding Fixture Design Process
A professional fixture design process generally includes the following steps:
- Process and part analysis
- Referencing strategy and locator layout design
- Selection of clamping systems (manual, pneumatic, hydraulic)
- Robot reach and welding torch angle analysis
- Collision and accessibility simulations
- Production drawings and technical documentation
- Commissioning and process validation
This approach ensures maximum production stability for both manual welding fixtures and robotic welding fixtures.
Robotic Welding Cell Design and Integration
With the transformation driven by Industry 4.0, robotic welding cell design and robotic automation integration have become critical competitive advantages in manufacturing facilities. Modern robotic welding cells require not only robot integration but also the coordinated design of positioner systems, transfer mechanisms, fixture automation, safety architecture, and production data monitoring infrastructure.
A properly designed robotic welding cell provides the following benefits:
- Standardized and repeatable weld quality
- Reduced operator dependency
- Higher production speed
- Process traceability
- Minimized error rates
- Increased production capacity
Simulation studies play a major role, particularly in automotive robotic welding cells and heavy-industry welding cell applications. Through offline robot simulation, reach analysis, collision detection, and cycle-time optimization can be verified before the production system is installed.
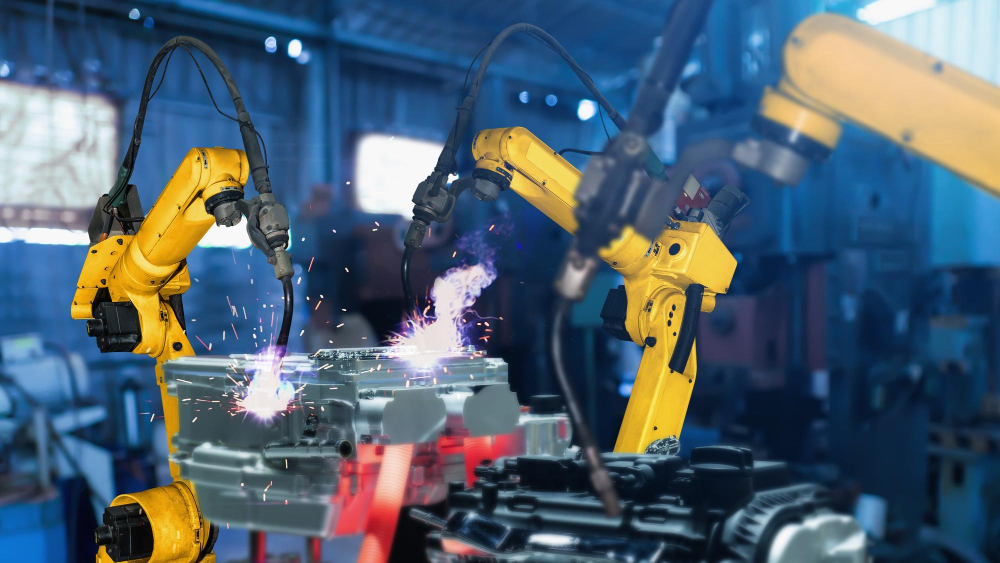

The Impact of Design and Simulation on Production Performance
Today, robot simulation, process simulation, and fixture design simulation have become essential components of modern manufacturing engineering. Simulation activities carried out during the design phase provide the following advantages:
- Significantly reduced commissioning time
- Lower revision and modification costs
- Minimized project risks
- More accurate production capacity planning
- High production performance from the very start of commissioning
For this reason, advanced engineering companies apply simulation validation as a standard engineering step in welding fixture design and robotic welding cell engineering processes.
Integrated Design Approach: Fixture + Robot + Process
The most successful modern production lines are developed through an integrated design approach where fixture design, robotic automation, and process engineering are handled together. This approach enables:
- Fixture designs optimized for robot accessibility
- Welding torch angles optimized during the design phase
- Integrated planning of part flow and line layout
- Verification of cycle time and production capacity targets during the design stage
This integrated engineering methodology is a critical success factor, particularly in high-volume automotive production lines and rail system projects.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive manufacturing environment, improving production efficiency requires more than equipment investment alone. Successful projects are built upon strong welding fixture design, properly engineered robotic welding cell design, and a comprehensive process engineering approach.
Fixture and robotic welding systems developed with the right engineering infrastructure provide long-term dimensional stability, high production capacity, and sustainable manufacturing performance across production lines for many years.